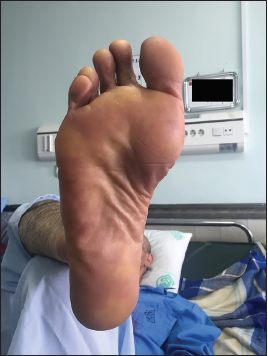
Palmoplantar Erythrodysesthesia Syndrome (PPES) caused by chemotherapeutic agents is rarely life threatening and requires a reduction in dose or discontinuation of chemotherapy. The use of cytarabine and doxorubicin in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) along with voriconazole can potentially alter the metabolism of the drugs and cause some interactions. In this study, we presented a case of AML who received cytarabine and doxorubicin as a chemotherapy regimen and voriconazole as a prophylactic anti-fungal. In this combination, voriconazole probably inhibits the P-glycoprotein pump, which leads to an increase in the cytarabine concentration. The emphasis of this report is the awareness of clinicians and pharmacotherapists about these interactions.
Cite this article as: Tavakoli-Ardakani M, Haghighi S, Shokouhi S, et al. Cytarabine and Doxorubicin-Induced Palmoplantar Erythrodysesthesia Syndrome: The Possible Role of Voriconazole Interaction. Eurasian J Med 2019; 51(3): 313-5.

.png)
_In%20Progress-1%20(1)_page-0001.jpg)

.png)
.png)