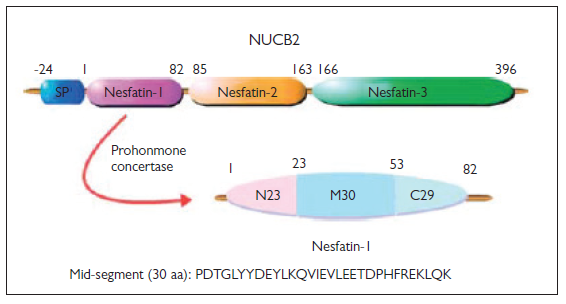
Metabolic syndrome is associated with a group of conditions abdominal obesity, high triglyceride levels, reduction in low-density lipoprotein, increased blood pressure, and increased fasting blood glucose. Hence, it poses a risk for type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome increases with age. Nesfatin-1, which affects different systems, has recently been discovered as a regulatory peptide molecule. With the discovery of nesfatin-1, it has been reported to inhibit the intake of nutrients and have significant regulatory effects on energy metabolism. As nesfatin-1 is present in both central and peripheral tissues, it is thought to have many functions. In addition to its suppressive effect on food intake, nesfatin-1 has also been reported to have an effect on the blood glucose level for regulating cardiac functions and affecting obesity by providing weight loss. Considering the effects of nesfatin-1, it may be associated with metabolic syndrome.
Cite this article as: Tekin T, Çiçek B, Konyalıgil N. Regulatory Peptide Nesfatin-1 and its Relationship with Metabolic Syndrome. Eurasian J Med 2019; 51(3): 280-4.

.png)
_In%20Progress-1%20(1)_page-0001.jpg)

.png)
.png)